Cheating in video games, including Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO), is a major concern in the gaming community. Cheating undermines fair play and disrupts the balance of the game, thus spoiling the experience for everyone involved.
Different forms of cheating in CS:GO include but are not limited to: using aimbots (software that automatically targets opponents), wallhacks (software that allows players to see through walls), or other forms of hacks that give unfair advantages.
To counteract this, Valve, the developer of CS:GO, has implemented a number of measures to detect and punish cheaters:
- VAC (Valve Anti-Cheat System): VAC is the primary anti-cheat solution used by Valve. It is an automated system designed to recognize cheats installed on users’ computers. If a user connects to a VAC-secured server from a computer with identifiable cheats installed, the VAC system will ban the user from playing on VAC-secured servers in the future.
- Overwatch System: This is a peer review system where experienced players can review reports of suspicious behavior. If a player is found to be cheating by the overwatch community, they can be banned.
- Trade Bans: Trade bans may be enacted on accounts that are involved in scamming other users or are found to be trading in-game items that were gained through cheating.
Players found cheating in CS:GO can face a variety of penalties:
- Temporary or Permanent Bans: Cheaters can be temporarily or permanently banned from playing the game on official servers. The length of the ban depends on the severity and frequency of the offense.
- Loss of Trust Factor: CS:GO uses a Trust Factor system to pair players in matchmaking. If a player is caught cheating, their Trust Factor can decrease, resulting in longer matchmaking times and pairing with other players who also have low Trust Factors.
- Account Deletion: In some severe cases, Valve may decide to delete the cheater’s Steam account altogether.
- Loss of In-Game Items: Players may also lose any items they have earned or purchased in the game.
It’s also worth noting that many third-party competitive leagues and tournaments have their own anti-cheat systems and cheating penalties, which can be even stricter than those enforced by Valve.
As an additional note, in the gaming community at large, being labeled as a cheater can have social repercussions, as it often leads to exclusion from certain groups or activities. It’s always advisable to play games in the spirit of fair competition.
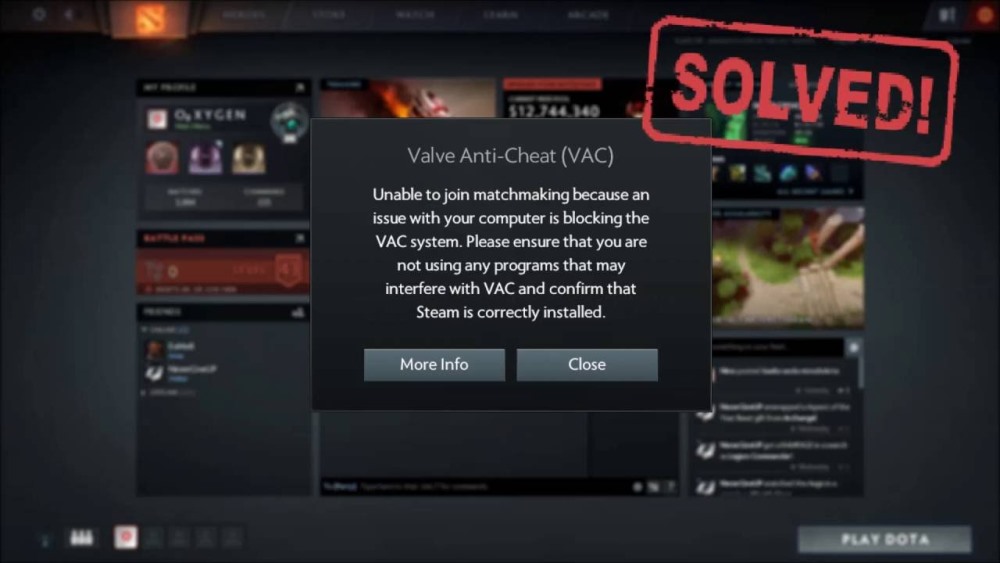
VAC (Valve Anti-Cheat System)
Valve Anti-Cheat, commonly abbreviated as VAC, is an anti-cheat solution developed by Valve Corporation as a component of the Steam platform. It was first introduced with Counter-Strike in 2002.
VAC works by scanning a user’s computer for cheats when they connect to a VAC-secured server. This could include known cheats (blacklisted software), cheat signatures (unique identifiers found in cheat programs), or anything else that may interfere with the normal operation of the game in ways not intended by the developers.
VAC is designed to be an automated system that bans users who are detected cheating. When a user is banned by VAC, they will receive a notification in their Steam profile, and the ban becomes permanent and unappealable. This means that they cannot play on VAC-secured servers for the game they were banned from. The bans are also linked to the user’s Steam account, so buying a new copy of the game won’t allow them to bypass the ban.
One unique aspect of VAC is that it does not ban cheaters immediately after detection. Instead, it implements delayed bans, typically a few days to several weeks after the cheat has been detected. This is to make it harder for cheat developers to test if their cheats are detectable by VAC.
It’s important to note that VAC does not ban based on reports from other users, but from cheat detection software running on the player’s computer. However, the game Counter-Strike: Global Offensive has implemented a system called “Overwatch” that allows experienced community members to review reports of disruptive behavior, independent of VAC.
While VAC has been effective in tackling cheats for Valve games, it’s not infallible. Cheat developers continually evolve their methods to evade detection, and there are some cheats that VAC may not be able to detect. As such, it’s part of an ongoing arms race between cheat developers and anti-cheat solutions.
Overwatch System
The Overwatch system is a feature in Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO) that was introduced by Valve to aid in the detection and prevention of cheating. It leverages the experience and knowledge of the community to maintain the integrity of the game.
The way the Overwatch system works is as follows:
- The Report: When a player notices suspicious activity from another player in a match, they can report this behavior. This can be anything from aimbotting (using a software that improves aiming) to wallhacking (using a software that allows a player to see through walls), and more.
- The Case: If a player gets reported multiple times, an “Overwatch Case” is made. This includes snippets of gameplay (typically about 8 rounds of a match) where the reported player’s behavior is shown from their perspective. The identity of the player in question is kept anonymous.
- The Investigators: Players who have been in the game for a while and have a clean record can become “Investigators.” They can review Overwatch cases and judge whether the player in question is cheating. They will not know who reported the player, who the player is, or what they were specifically reported for.
- The Verdict: The investigators give their verdict on whether they think the player was cheating or not. If enough investigators agree that a player was cheating, the player will receive a ban. The more accurate an investigator’s verdicts are, the more weight their future verdicts will carry.
The Overwatch system is essentially a community-driven approach to identifying and punishing cheaters in CS:GO. It allows experienced players to help maintain the game’s integrity by identifying potential cheaters for further review. It’s an additional measure on top of Valve’s Anti-Cheat (VAC) system, designed to catch cheaters that might otherwise slip through the cracks.
Trade Bans
Trade bans, also known as Steam Trading bans, are imposed by Valve to prevent fraudulent activity and protect the integrity of the Steam community. They’re typically enforced when a user conducts activity contrary to Steam’s trading policies or engages in scams or fraudulent trade practices.
A trade ban prevents a Steam account from using the Steam Community, including trading and using the Steam Market.
An account can be trade banned for a few different reasons:
- Scamming: If a user is found to have scammed another user, they will receive a trade ban.
- Abusing the Steam Trading System: If a user is found to be abusing the trading system in any way, for example by farming items to sell on the market, they can be trade banned.
- Purchasing Items with a Fraudulent Payment Method: If a user purchases items with a stolen credit card, or conducts any form of fraudulent payment activity, they can be trade banned.
- Cheating: In games like CS:GO, users who are found to have cheated or have had their accounts compromised (and subsequently used for cheating) may have their inventories locked, preventing them from trading or selling items.
Trade bans can be temporary or permanent, depending on the severity of the violation. Temporary trade bans can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks, while permanent trade bans last indefinitely.
Appealing a trade ban is typically difficult. Valve asserts that trade bans are only applied in extreme cases where they are 100% certain of the user’s violation, so they will not be lifted unless Valve believes they were applied by mistake.
Valve encourages users to remain vigilant and take precautions when trading, to avoid falling victim to scams that could result in a trade ban.
Temporary or Permanent Bans
In games like Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO), both temporary and permanent bans can be issued depending on the severity and frequency of a player’s violation.
These bans can result from various actions that disrupt the game’s fair play principles and community standards.
- Temporary Bans: Also known as “cooldowns,” these are issued for less serious or first-time offenses.
They can range from a few minutes to several days or weeks. Common reasons for temporary bans include:
- Disconnecting from matches: Players who frequently disconnect or abandon competitive matches can receive temporary bans to discourage such behavior.
- Team killing or team damaging: If a player repeatedly kills or injures their teammates, they can receive a temporary ban.
- Griefing: If a player intentionally disrupts or harasses their teammates, they can receive a temporary ban.
- Cheating: In some cases, suspected cheating can lead to temporary bans pending investigation.
- Permanent Bans: These are more severe and are issued for serious or repeated offenses. Once a player is permanently banned, they’re typically barred from playing the game on official servers indefinitely.
Common reasons for permanent bans include:
- Cheating: If a player is found to be using hacks, aimbots, or any form of cheating software, they can receive a permanent ban.
- Scamming: Players who engage in fraudulent activity or scam others, especially in relation to in-game items or skins, can receive a permanent ban.
- Exploiting: If a player discovers and uses a game exploit to gain an unfair advantage over other players, they can receive a permanent ban.
The VAC (Valve Anti-Cheat) system enforces these bans automatically if it detects cheat software, while the Overwatch system in CS:GO can lead to bans based on peer review of reported misconduct.
Permanent VAC bans in particular are non-negotiable and cannot be removed by Steam Support. If a VAC ban is determined to have been issued incorrectly, it will automatically be removed. Players are responsible for any actions taken on their account, so a ban issued for an infraction by a friend or family member who had access to the account will still apply.
While bans are a necessary enforcement tool, the goal is to encourage fair and respectful gaming experiences for everyone, discouraging disruptive behavior and cheating.
Loss of Trust Factor
The Trust Factor in Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO) is a system implemented by Valve to provide a better matchmaking experience for players. This system uses a variety of factors to determine a player’s Trust Factor score, then uses this score to match them with other players with similar scores.
The exact mechanics of how Trust Factor is calculated remain a secret to prevent manipulation, but it takes into account factors such as:
- The time a player has spent playing CS:GO and other games on their Steam account.
- The frequency at which they’ve been reported for misconduct.
- Whether they’ve been marked by the Overwatch system.
- The frequency of their game purchases, returns, and chargebacks on Steam.
- Whether they’re frequently playing with or against players who have been banned.
If a player is found to be cheating, their Trust Factor score can be significantly reduced. This means that they’re more likely to be matched with and against other players who also have a low Trust Factor. This serves as a form of punishment, as games with low Trust Factor players tend to have more cheaters and generally be of lower quality.
However, a low Trust Factor is not permanent. Players can improve their Trust Factor by playing legitimately and being a positive member of the CS:GO community. This includes not cheating, being respectful to other players, and avoiding actions that could get them reported or banned.
It’s also worth noting that players have the option to queue for games that exclusively use Trust Factor for matchmaking, which helps to improve the overall quality of their matches by matching them with players who have demonstrated a similar level of trustworthiness.
Account Deletion
Account deletion or termination is a severe penalty that can be enforced by digital platforms like Valve’s Steam if a user engages in particularly egregious violations of their user agreement or terms of service. It’s important to note that Valve tends to reserve such measures for the most serious offenses, as this is a drastic step.
While cheating in a game can lead to a variety of penalties such as temporary or permanent game bans, trade bans, or a reduced trust factor, it typically doesn’t result in account deletion, unless the violation is particularly extreme or involves additional elements like fraud, scamming, or other forms of misuse of the platform.
When an account is deleted:
- Access is Revoked: The user loses all access to their account. They will not be able to log in, play games, or use any Steam services.
- Loss of Purchased Items: All games and other items purchased through the Steam store on the account are lost. This includes not only games, but also downloadable content (DLC), in-game items, skins, etc.
- Loss of Community Features: The user loses the ability to participate in the Steam community, including forums, market transactions, trading, etc.
- Irreversibility: Once an account is deleted, the process cannot be reversed. The user will have to create a new account if they want to use Steam services again, and they will not be able to recover any of the games or other content from their deleted account.
Again, it’s worth reiterating that account deletion is a last resort, used in the most extreme cases. Regular or occasional cheating in a game like CS:GO is more likely to result in game-specific punishments, such as VAC bans or reduced Trust Factor, rather than a full deletion of the user’s Steam account.
Loss of In-Game Items
When a player is caught cheating in a game like Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO), one of the potential penalties that they can face is the loss of in-game items. This penalty is primarily intended to deter cheating by adding a tangible cost to being caught.
In CS:GO, in-game items include weapon skins, stickers, and other cosmetic items that don’t affect gameplay but are highly sought after for their aesthetic appeal. Some of these items can be quite valuable, either because they’re rare, have a desirable pattern or color scheme, or because they’re associated with a significant event like a major tournament.
If a player is caught cheating, their CS:GO inventory can be locked, preventing them from trading or selling their items on the Steam Market. This effectively makes the items worthless, as their value primarily comes from their tradability.
In severe cases, Valve can even delete items from a player’s inventory. However, this is less common, as locking the items generally serves the same purpose of preventing the player from profiting from their cheating.
The loss of in-game items can therefore be a significant penalty, particularly for players who have invested a lot of time or money into collecting rare or valuable items. This adds an additional deterrent against cheating, as players stand to lose not just their ability to play the game, but also their in-game items.